
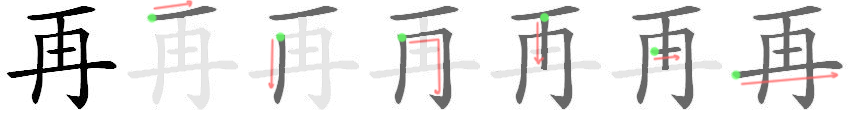
If you are studying kanji, don’t lose the opportunity to learn them with the correct stroke order.

learning kanji will become a lot more difficult and time consuming.you will never learn to read cursive Japanese.If you don’t know the correct stroke order: It’s not something you should ignore or leave to your imagination. SO rule 9: horizontal vs hidariharai, short firstįor many reasons, it is very important to know the correct stroke order of each kanji.
#Wo stroke order how to
#Wo stroke order code
the code stroke, although not the most technically demanding radiological protocol, can be a high-stress situation with a variety of extrinsic factors weighing on the radiographer and surrounding healthcare teams.See: CT angiography of the cerebral arteries (technique) Practical points It should be noted that there is increased interest in the use of multiphase CTA particularly to accurately assess the degree of collateral circulation 3. aneurysms and arteriovenous malformations.It not only allows for the visualization numerous intracranial features relevant to the stroke setting but also anatomy that may be relevant to the endovascular intervention. It is performed using the arterial phase of intravascular contrast. The last component is CT angiography usually performed from the arch or the aorta to the vertex of the skull. These allow not only the diagnosis and quantification of areas of impaired perfusion but also the identification of infarct core and penumbra that are important in selecting patients for thrombolysis/ endovascular clot retrieval. time-to-maximum (Tmax) or time to peak (TTP).Intravenous contrast is then administered and various parameters of cerebral perfusion calculated. tumors) it specifically allows for the following stroke-related features to be sought: In addition to a rapid overview of the brain (see an approach to CT head) that may demonstrate unexpected non-stroke findings (e.g. Furthermore, even if known, with the exception of severe life-threatening allergy, complications of contrast administration may be deemed less important than the appropriate assessment of the stroke.Ī non-contrast CT of the brain, usually obtained volumetrically and reformated in three planes (sagittal, axial and coronal), is obtained first. It is important to note, however, that in the hyperacute setting of evolving stroke, this information is not always known. ContraindicationsĪs is the case with other contrast studies, contraindications, such as chronic renal failure and allergy may be important. There is an increasing trend to perform multi-pass CTA of the brain to perform multiphase CT angiography collateral score in acute stroke.
It should be noted that this is not uniformly accepted and some centers do not perform perfusion routinely 3. CT angiography (aortic arch to the vertex of the skull).To achieve this, stroke protocol CT usually includes 3 concatenated scans 2: to assess vascular anatomy that may impact endovascular access.to identify the location and physiological effects of arterial blockage.to assess the brain for established infracts or alternative diagnoses.The purpose of this protocol is three-fold: In most centers, CT is favored over MRI in the ultra-acute setting due to time and access constraints, despite acknowledging that MRI, and particularly diffusion-weighted imaging, is superior in identifying small infarcts and defining infarct core 1-3. endovascular clot retrieval or intravenous thrombolysis). A CT stroke protocol is obtained in the emergency setting to rapidly diagnose and quantify patients presenting with probable ischemic strokes and to enable appropriate urgent management (e.g.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
